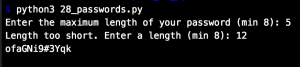
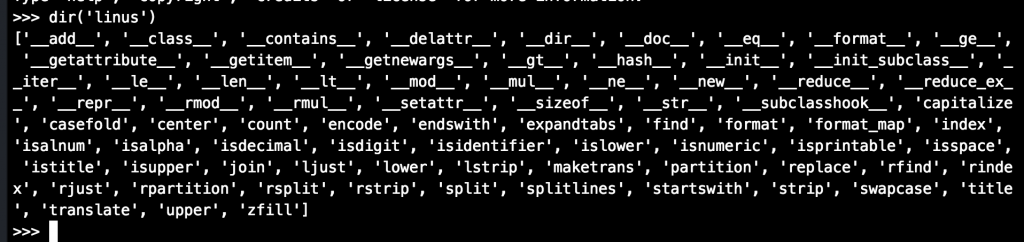
The shell command dir lists all attributes an object has – and remember everything in Python is an object.
Start your terminal and enter „python“ to start the IDLE mode. Then type for example dir(‚linus‘) and you will
get all the attributes for „linus“ which in this case is a string.
Pretty neat isn’t it? But that’s not all Python will do for you. The help-function will deliver even deeper information
about other functions. We can use it on the command ‚linus‘.lower for example like this:
help(‚linus‘.lower)
Here is the output:
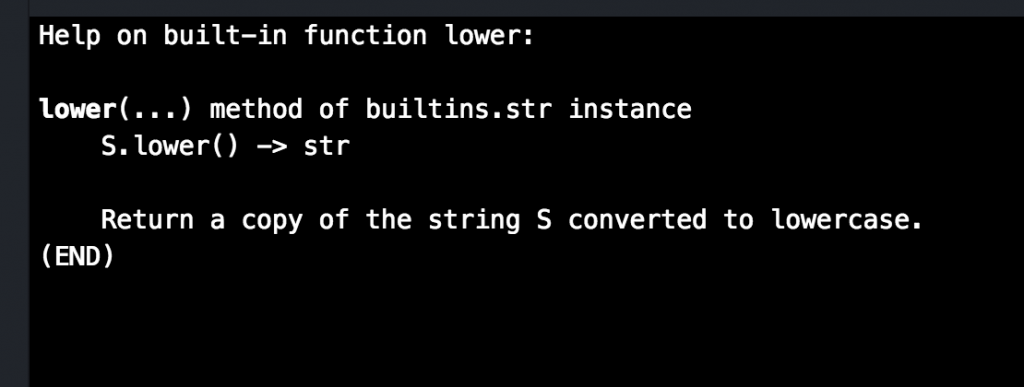
The help-function returns information about virtually everything in Python.
Your Python comes with its own Docs installed – amazing!
And there is even more you say? Yes indeed! With pdb Python has its own integrated debugger!
With the debugger you can go through your code line by line and look up any possible bugs!
To use pdb you will have to include the following lines in the code.
import pdb
pdb.set_trace()
Once you run the program the execution will stop once the interpreter comes across the pdb.set_trace() command.
You will be redirected to the shell where you can go through every line manually and see how your
code behaves. With „n“ or „next“ you can jump to the next line of code.
pdb can do a lot more for you actually. You find the complete documentation here